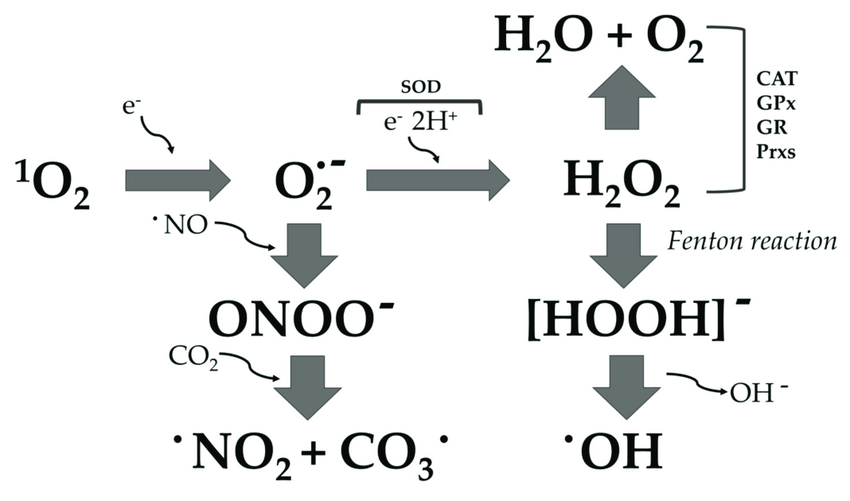
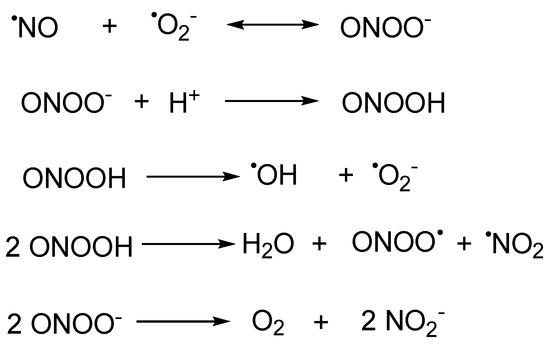
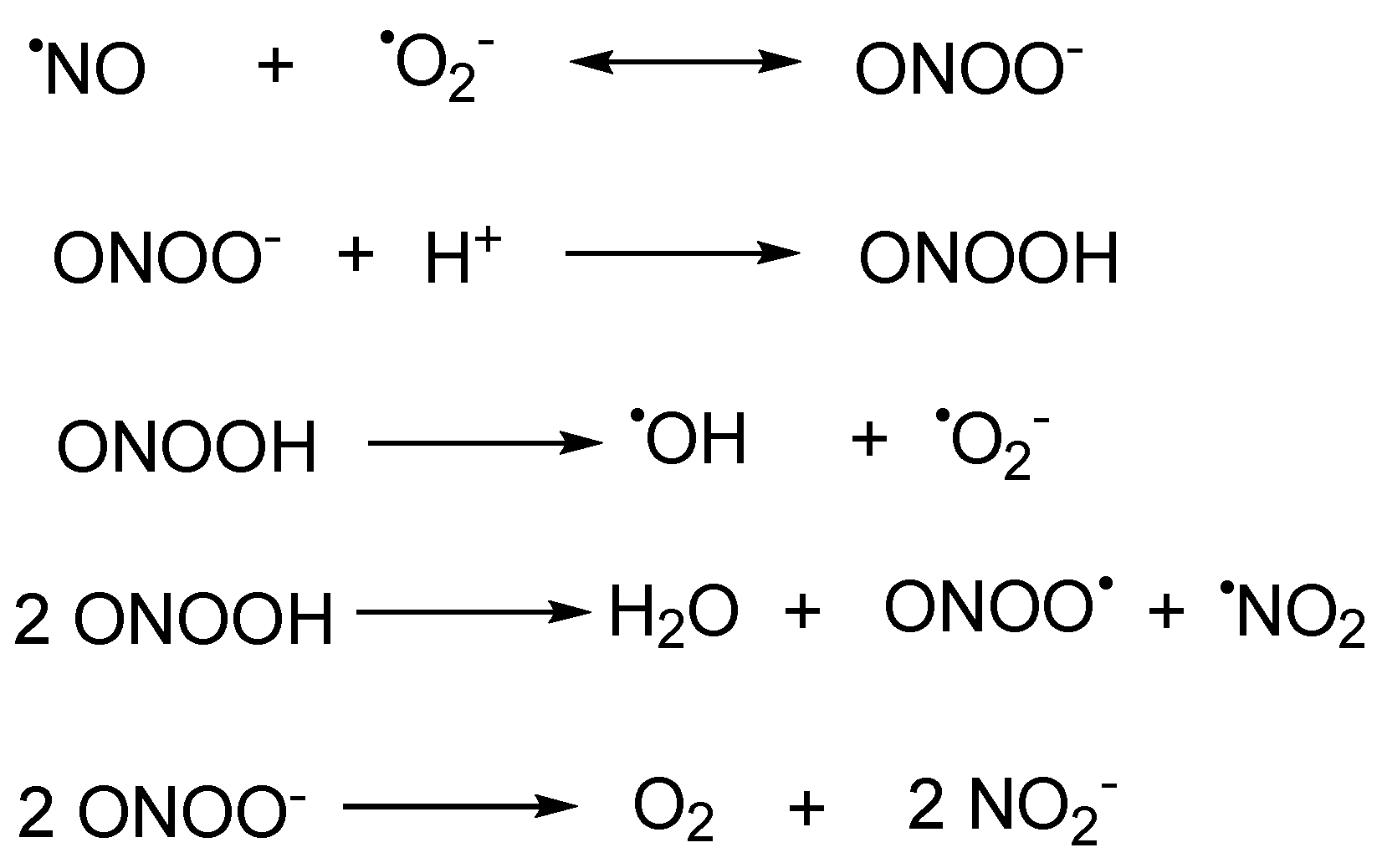CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages, MPO

Download scientific diagram | CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages, MPO, and ONOO ؊ . a, mitochondria (2 mg) were incubated in the presence of NO 2 Ϫ (0.25–1.0 m M ) and supplemented with various fatty acids (1 M ). Lipids were extracted, and NO 2 -FA was quantified by HPLC-MS/MS using [ 13 C 18 ]NO 2 -LA as internal standard. Results represent the mean Ϯ S.D. ( n ϭ 3), * indicates significantly different ( p Ͻ 0.05) from control without fatty acid addition. b, NO 2 -CLA formation from endogenous CLA and the concomitant CLA consumption was quantified by HPLC-MS/MS in mitochondria (2 mg) incubated with NO 2 Ϫ (1 m M ) at pH 6 ( n ϭ 3). c, chromatogram showing forma- from publication: Conjugated Linoleic Acid Is a Preferential Substrate for Fatty Acid Nitration | The oxidation and nitration of unsaturated fatty acids by oxides of nitrogen yield electrophilic derivatives that can modulate protein function via post-translational protein modifications. The biological mechanisms accounting for fatty acid nitration and the specific | Conjugated Linoleic Acid, Fatty Acids and Nitrate | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Activation of Thromboxane A2 Receptor (TP) Increases the

Discovery of bioactive nitrated lipids and nitro-lipid-protein

Redox Signaling by Reactive Electrophiles and Oxidants

CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages
Morphological transformation in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with
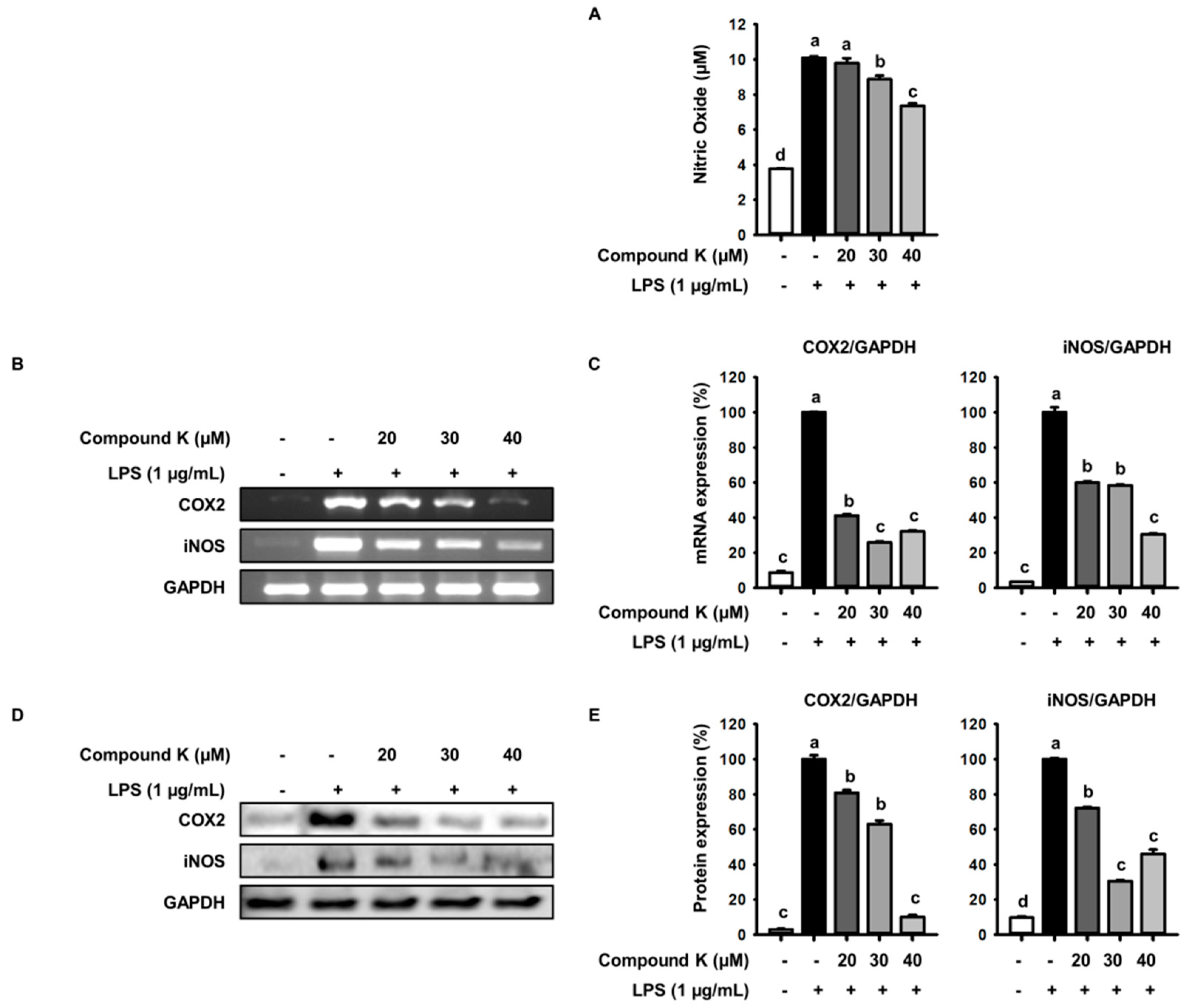
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
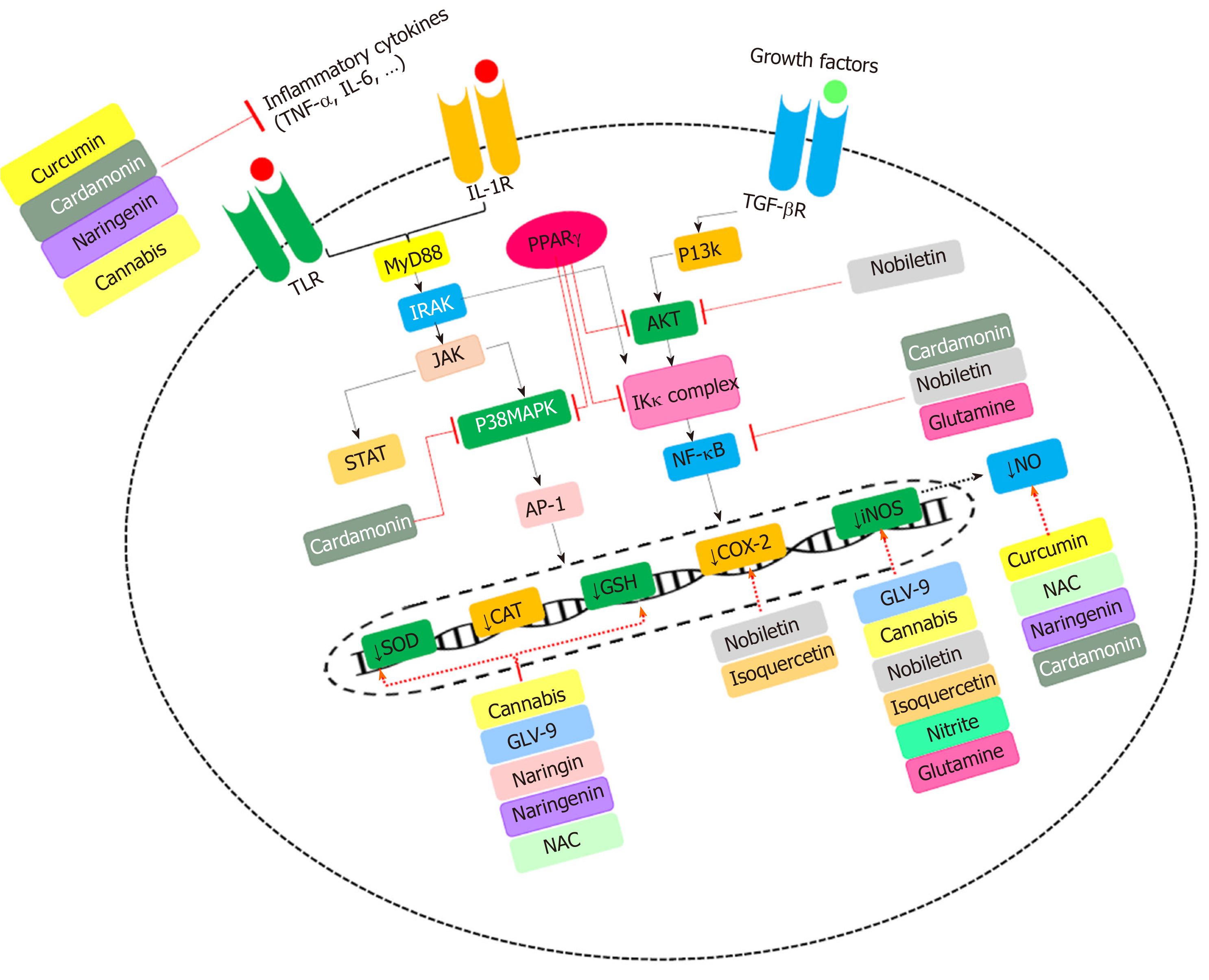
Interventions of natural and synthetic agents in inflammatory

Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation

JCI - Mitochondrial dysfunction in macrophages promotes

CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages