Tick‐borne encephalitis virus and LIV transmission involves a complex

Download scientific diagram | Tick‐borne encephalitis virus and LIV transmission involves a complex ecology of reservoir species, ticks and indicator species that support tick populations. Small vertebrates including rodents, insectivores, and wild carnivores serve as amplifying reservoirs, developing high titer viremia and transmitting to ticks. Ticks transmit transstadially through egg, larvae, nymph, and adults, and transmit to a wide variety of vertebrate species. Large mammals such as deer and livestock maintain tick populations and are susceptible to disease, but do not transmit back to ticks due to low virus load, short duration of viremia or a combination of the 2. They are considered indicator species because they are valuable sentinel species for disease and antibody prevalence. Humans and horses are considered accidental hosts because they are not involved in sustaining transmission or feeding tick populations from publication: European College of Equine Internal Medicine consensus statement on equine flaviviridae infections in Europe | Horses and other equids can be infected with several viruses of the family Flaviviridae, belonging to the genus Flavivirus and Hepacivirus. This consensus statement focuses on viruses with known occurrence in Europe, with the objective to summarize the current literature and | Flaviviridae, Hepacivirus and Internal Medicine | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
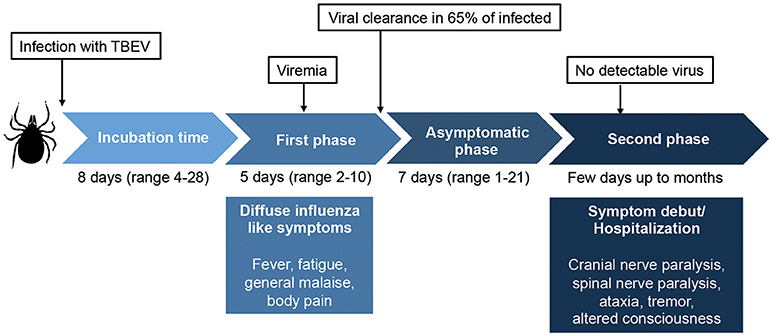
Frontiers Cell-Mediated Immune Responses and Immunopathogenesis of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus-Infection
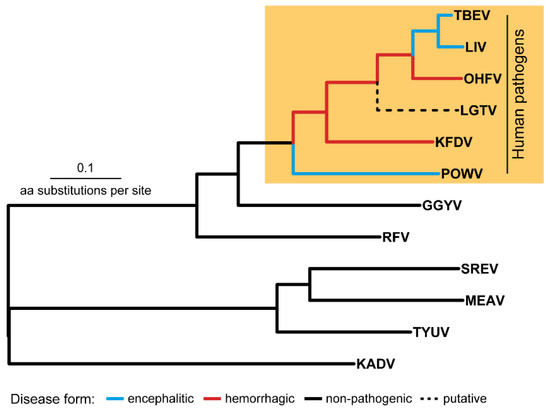
IJMS, Free Full-Text

TICKBORNE DISEASES OF THE UNITED STATES

Lyme Disease - Infectious Diseases - Merck Manuals Professional Edition
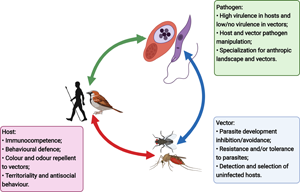
Evolutionary consequences of vector-borne transmission: how using vectors shapes host, vector and pathogen evolution, Parasitology

Tick-borne encephalitis virus - Wikipedia

Secreted NS1 proteins of tick-borne encephalitis virus and West Nile virus block dendritic cell activation and effector functions
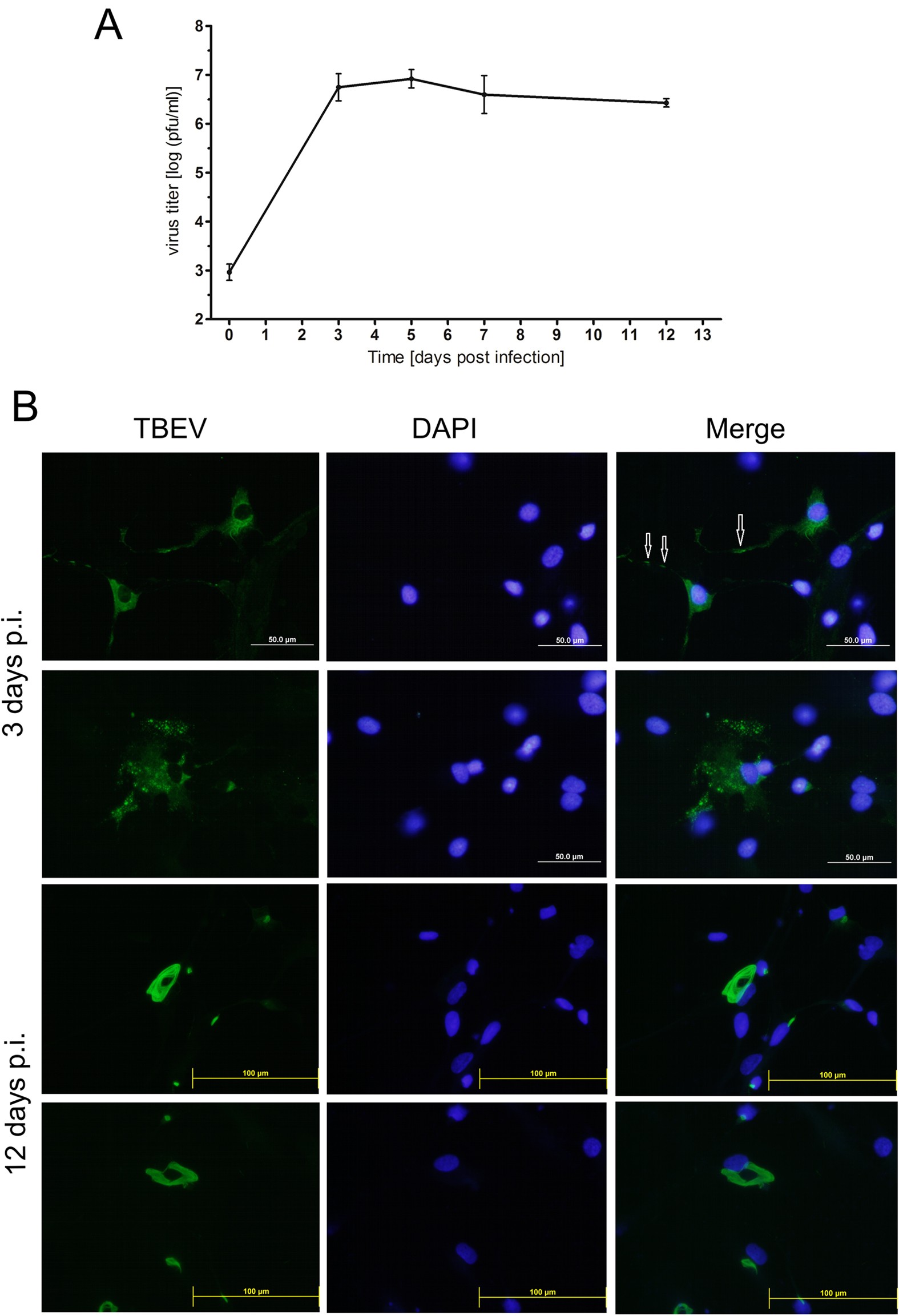
Electron Tomography Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Human Neurons

Tick‐borne encephalitis virus and LIV transmission involves a complex
Pathogens and Vectors - TROPIQ









