Figure 6 from Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease.

FIG. 6. The interplay of nitric oxide, superoxide, peroxynitrite, and nitrogen dioxide. When nitric oxide and superoxide are both present, they may also react with nitrogen dioxide to form N2O3 and peroxynitrate. Peroxynitrate decomposes to give nitrite and oxygen, while N2O3 can react with thiols to give nitrosothiols or with hydroxide anion to give nitrite. Goldstein et al. (452) showed that it also reacts at a diffusion-limited rate with peroxynitrite to yield two molecules of nitrogen dioxide and one of nitrite. This creates a cycle to generate more nitrogen dioxide when bolus additions of peroxynitrite are added at neutral pH and substantially increases the number of potential reactions occurring. These same reactions will also occur in vivo, particularly when nitric oxide is produced faster than superoxide. - "Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease."

Figure 6 from Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease

Oxidative stress in vascular cells. Nitric oxide (NO) and
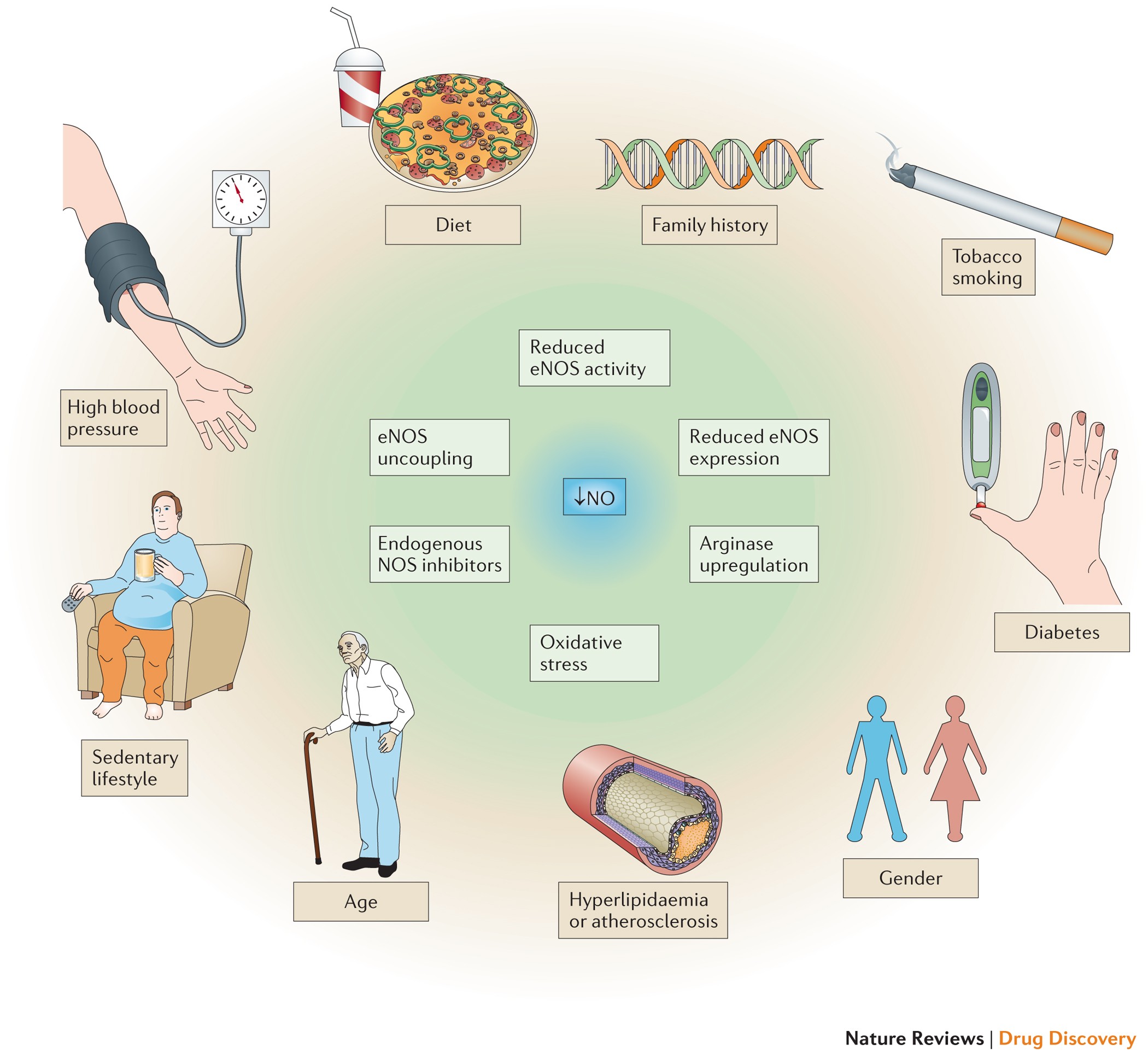
Strategies to increase nitric oxide signalling in cardiovascular
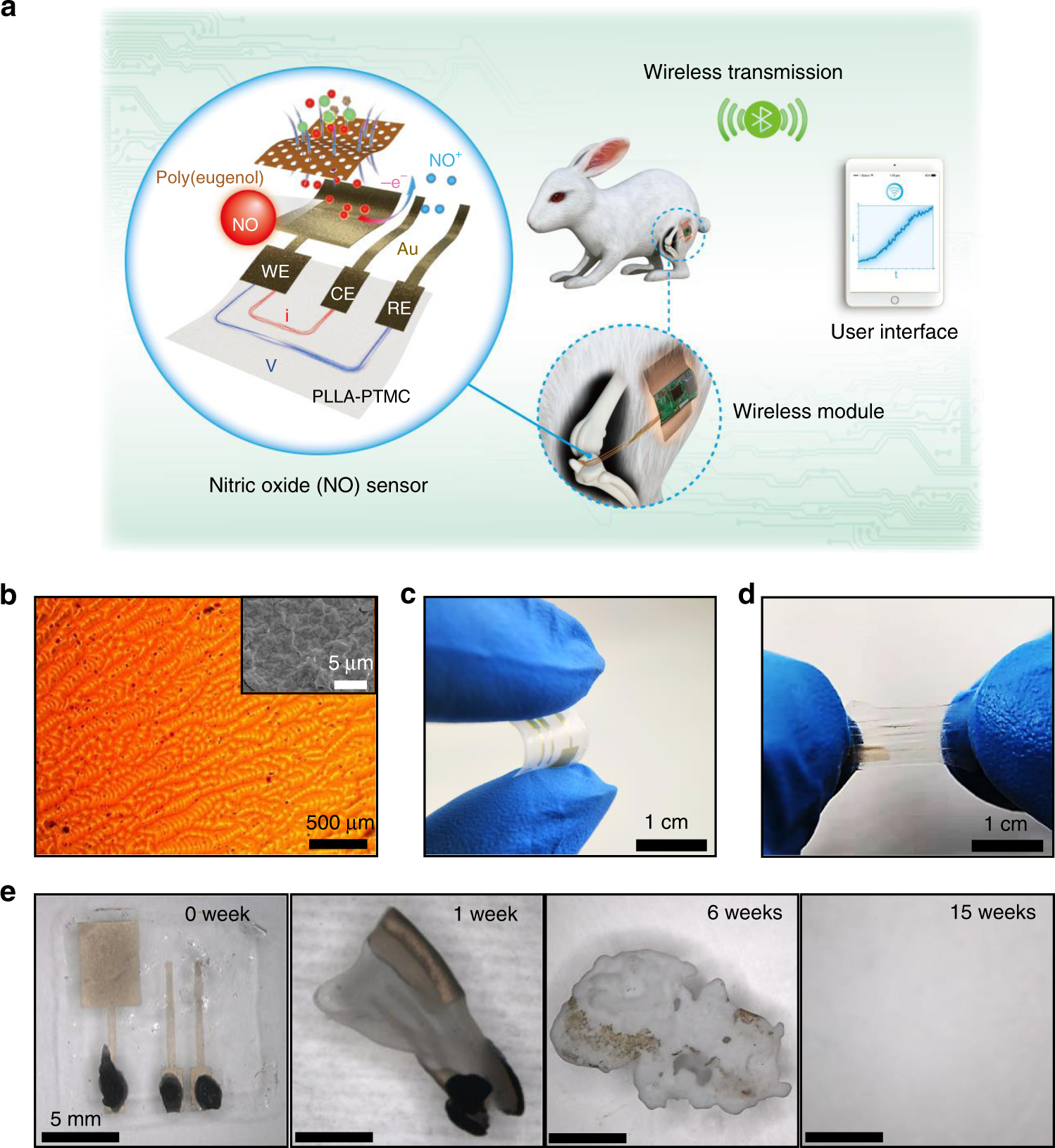

A flexible and physically transient electrochemical sensor for

The Antioxidant/Nitric Oxide-Quenching Agent Cobinamide Prevents
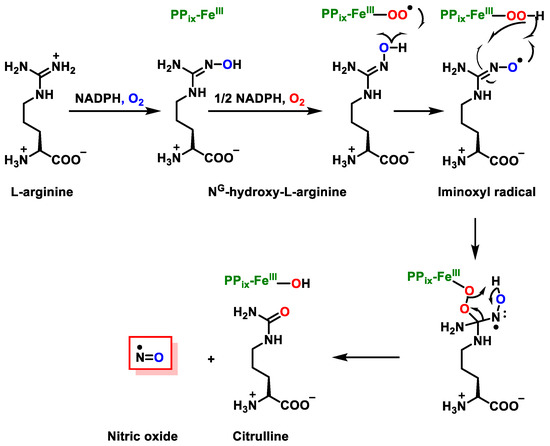
Stresses, Free Full-Text

Interactions of Homocysteine, Nitric Oxide, Folate and Radicals in

Figure 6 from Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease

Oxidation of NADH in the presence of constant superoxide

Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration
Cureus Nitric Oxide in the Management of Respiratory

Dietary Nitrate from Plant Foods: A Conditionally Essential

Full article: Peroxynitrite: cellular pathology and implications

Formation of peroxynitrite and nitrative damage. (a) Peroxynitrite

The reaction of peroxynitrite and carbon dioxide results in the