A reaction scheme showing the synthesis of silica nanoparticles

Download scientific diagram | A reaction scheme showing the synthesis of silica nanoparticles from TEOS; Reaction (1) includes the hydrolysis of TEOS to form silicic acid, followed by reaction (2) which involves the condensation of the silicic acid to produce silica nanoparticles with siloxane bridges (Si-O-Si). from publication: Silica Nanoparticles in Transmucosal Drug Delivery | Transmucosal drug delivery includes the administration of drugs via various mucous membranes, such as gastrointestinal, nasal, ocular, and vaginal mucosa. The use of nanoparticles in transmucosal drug delivery has several advantages, including the protection of drugs against | Silica Nanoparticles, Drug Delivery and Synthetic Methods | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Functionalized Silicas for Metal‐Free and Metal‐Based Catalytic Applications: A Review in Perspective of Green Chemistry - Rajendran - 2020 - The Chemical Record - Wiley Online Library

Silica nanoparticles for the layer-by-layer assembly of fully electro-active cytochrome c multilayers, Journal of Nanobiotechnology
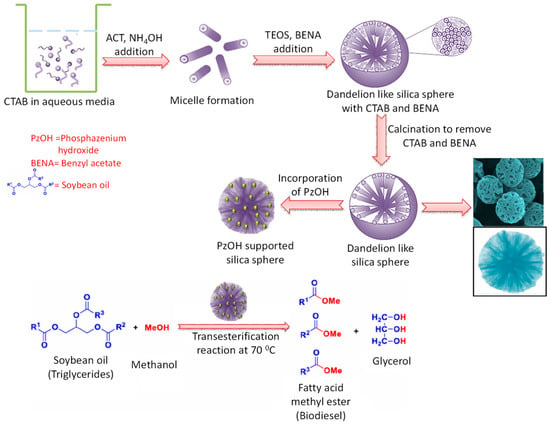
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text
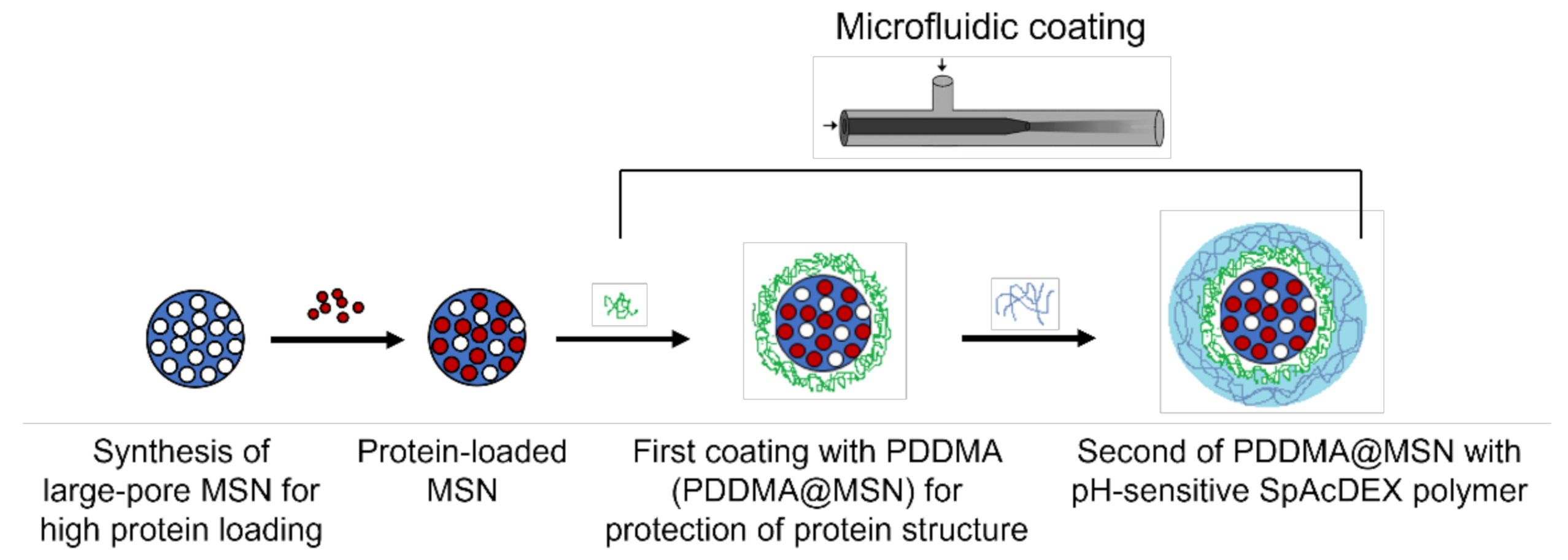
Biosensors, Free Full-Text

Synthesis of Silicon Nanoparticles from Rice Husk and their Use as Sustainable Fluorophores for White Light Emission

Sodium hydroxide catalysed silica sol-gel synthesis: Physicochemical properties of silica nanoparticles and their post-grafting using C8 and C18 alkyl-organosilanes - ScienceDirect

Green and sustainable synthesis of silica nanoparticles

Multidisciplinary Role of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Brain Regeneration and Cancers: From Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier to Treatment - Mendiratta - 2019 - Particle & Particle Systems Characterization - Wiley Online Library
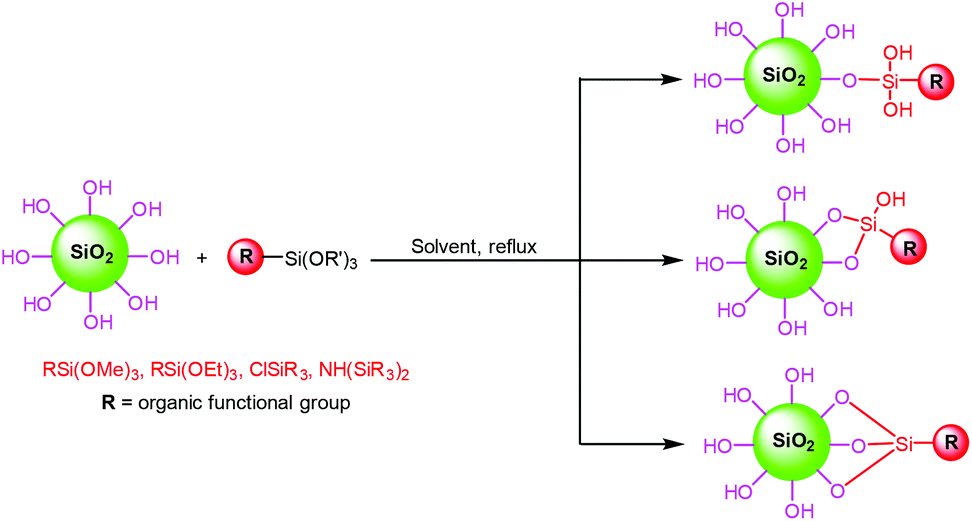
Functionalized silica nanoparticles: classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications - Nanoscale (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1NR04048K









